These effects typically have two types. 21 has two values defined as an external manipulation that either slows down value of Low or speeds up value of High the processing of each stimulus.
9 1 Setting Up A Factorial Experiment Research Methods In Psychology
Other than these slight detractions a factorial design is a mainstay of many scientific disciplines delivering great.

. Factorial research designs have more than one IV. The main disadvantage is the difficulty of experimenting with more than two factors or many levels. A factorial design that includes both an experimental independent variable IV and a nonexperimental participant PV.
Further these independent variables usually have more than level. Always achieves greater statistical power. Identify the true and false statements about experiments with more than one independent variable.
Always requires more subjects. Some of the combinations may not make sense from a policy or administrative. Its clear that factorial designs can become cumbersome and have too many groups even with only a few factors.
Sign in to download full-size image. What is an IV X PV design. Has two or more dependent variables.
A factorial design cannot have more than three independent variables. Figure 313 It is often useful to have more than one dependent variable. Variable values are orthogonally combined resulting in the four experimental conditions.
For example a researcher might choose to treat cell. Since factorial designs have more than one independent variable. The first is the factorial nature where there are two or more independent variables and each has two or more levels Stangor 2011.
General full factorial designs that contain factors with more than two levels. Both B and C. In much research you wont be interested in a fully-crossed factorial design like the ones weve been showing that pair every combination of levels of factors.
One limitation of the discussion is that it has focused on between-subjects designs. In a mixed factorial design one variable is altered between subjects and another is altered within subjects. In a factorial design the change in behavior due to the action of a single independent variable is called a n a.
Factorial designs have only one IV. Factorial design involves having more than one independent variable or factor in a study. The great advantage of factorial designs is that they disclose interactions between independent variables--they show how the relationship between y and is influenced by.
Variable 1 Low High Variable 2 Low High. Always requires more subjects. Always achieves greater statistical power.
The direct effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable. The repeated-measures factorial design is a quantitative method for exploring the way multiple variables interact on a single variable for the same person Field 2009. Another term you should be familiar with pertains to the number of levels involved in factorial.
Factorial designs allow researchers to look at. Factorial design involves having more than one independent variable or factor in a studyFactorial designs allow researchers to look at how multiple factors affect a dependent variable both independently and togetherFactorial design studies are. A factorial design always has more than one A.
Each factor in Fig. F More Than One Independent Variable The principal difference between a factorial experiment and a two-group experiment is that a factorial design a. A factorial design can have the different groups of subjects but it also manipulates more than one independent variable.
You can manipulate a lot of variables at once. While a between-subjects design has fewer threats to internal validity it also requires more participants for high statistical power than a within-subjects design. When an experiment tests all possible combinations of more than one independent variable it is often referred to as an factorial design.
IV X PV design. In this type of study there are two factors or independent variables and each factor has two levels. One common type of experiment is known as a 22 factorial design.
Factorial experiments often involve two or three independent variables but rarely more. Has more than one independent variable. Since factorial designs have more than one independent variable it is also possible to manipulate one independent variable between subjects and another within subjects.
A factorial design has to be planned meticulously as an error in one of the levels or in the general operationalization will jeopardize a great amount of work. The main disadvantage is the difficulty of experimenting with more than two factors or many levels. Factorial research designs are not common in the field of psychology.
Factorial designs can only utilize between subjects variables. These designs can show that the effect of one independent variable depends on the level of another independent variable also known as an interaction effect. However all else being equal the factorial designs will still have more power than the individual experiments and single factor approaches.
What are the pros and cons of a between-subjects design. The number of runs necessary for a 2-level full factorial design is 2 k where k is the number of factors. A main effect is the action or.
It is straightforward to extend every design here to incorporate repeated measures which will improve statistical power. A factorial design has to be planned meticulously as an. In a factorial design the main effects are A the effects of the most important independent variables on your dependent variable.
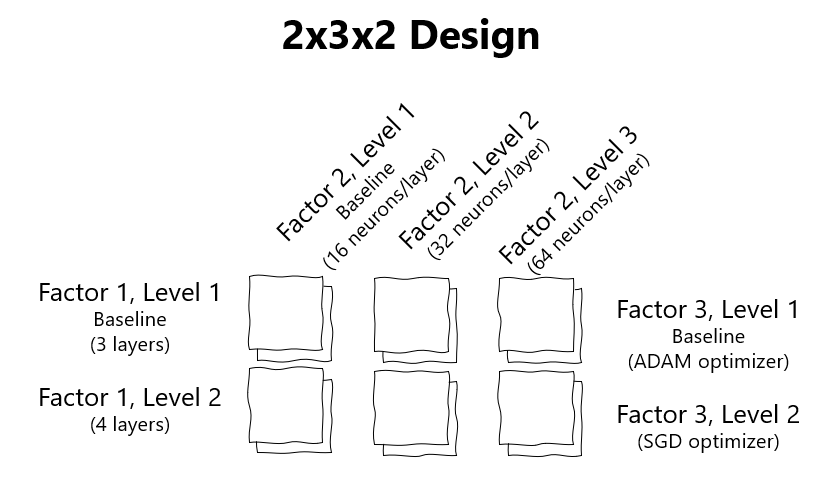
Each variable being manipulated is called a factor. A factorial design is one that looks at the effect of more than one independent variable. The number of digits tells you how many in independent variables IVs there are in an experiment while the value of each number tells you how many levels there are for each independent variable.
A participant variable is another type of manipulated variable. The within-subjects design is more efficient for the researcher and controls extraneous participant variables. This is called a mixed factorial design.
As the number of factors in a 2-level factorial design increases the number of runs necessary to do a full factorial design increases quickly. A 2 2 factorial design. This type of design is called a factorial design because more than one variable is being manipulated.
More demanding in terms of time and resources as compared to a multiple. What is IV vs PV. Level of a single independent variable.

Factorial Design Variations Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Solved Which Of The Following Is True About Factorial Chegg Com

Factorial Designs Research Methods Knowledge Base

Chapter 9 Factorial Designs Factorial Design Definition Two Or More Ivs Every Level Of One Iv Combined With Every Level Of Other Iv Ivs Called Ppt Download
Don T Forget About The Scientist In Your Data Scientist Title Part 2 By Kevin Mcgovern Towards Data Science

Factorial Design Variations Research Methods Knowledge Base

Solved Multiple Choices Each Question May Have More Than Chegg Com

0 comments
Post a Comment